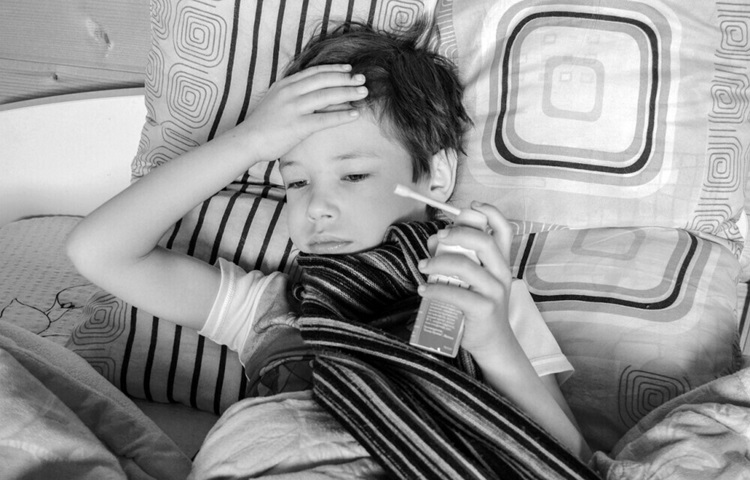
Inhalers are essential tools for managing respiratory conditions like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and other lung-related issues. Proper use of an inhaler ensures that medication is delivered effectively to the lungs, maximizing its therapeutic effects and minimizing side effects. This guide will break down the different types of inhalers and provide detailed instructions on how to use each type.
After reading this guide, if you would like more information about using inhalers or want to ask any inhaler related questions, try out Medidex Connect to instantly connect with a pharmacist online.
How to Use an Inhaler
Types of Inhalers
There are several types of inhalers, each designed to deliver medication in a specific way. The main types are:
- Metered-Dose Inhalers (MDIs)
- Dry Powder Inhalers (DPIs)
- Soft Mist Inhalers (SMIs)
- Nebulizers
Metered-Dose Inhalers (MDIs)
MDIs are the most common type of inhaler. They deliver a specific amount of medication in aerosol form through a propellant.
How to Use an MDI
- Preparation:
- Shake the inhaler well before each use.
- Remove the cap and inspect the mouthpiece to ensure it is clean.
- Priming (if necessary):
- Prime the inhaler by spraying it into the air once or twice if it’s the first use or hasn’t been used for a while.
- Using the Inhaler:
- Hold the inhaler upright with your thumb on the base and index and middle fingers on the top.
- Tilt your head back slightly and breathe out fully to empty your lungs.
- Place the mouthpiece in your mouth, creating a seal with your lips.
- Begin to breathe in slowly and deeply through your mouth while pressing down on the canister to release the medication.
- Continue to breathe in slowly and deeply until your lungs are full.
- Holding Your Breath:
- Remove the inhaler from your mouth and hold your breath for about 10 seconds to allow the medication to settle in your lungs.
- Breathe out gently.
- Cleaning:
- Clean the mouthpiece regularly with warm water to prevent medication buildup and blockage.
Dry Powder Inhalers (DPIs)
DPIs deliver medication in powder form, requiring the user to inhale with sufficient force to disperse the medication into the lungs.
How to Use a DPI
- Preparation:
- Remove the cap and ensure the device is ready for use.
- Load a dose of medication if necessary (some DPIs require you to load a capsule or twist a dial).
- Using the Inhaler:
- Breathe out fully, away from the inhaler, to avoid blowing moisture into the device.
- Place the mouthpiece in your mouth, forming a tight seal with your lips.
- Inhale quickly and deeply through your mouth, ensuring you breathe in the powder fully.
- Holding Your Breath:
- Remove the inhaler and hold your breath for about 10 seconds to allow the medication to settle.
- Breathe out slowly.
- Cleaning:
- Clean the mouthpiece with a dry cloth or tissue. Avoid using water as it can affect the powder.
Soft Mist Inhalers (SMIs)
SMIs release a fine mist of medication, offering a slower and more prolonged release compared to MDIs and DPIs.
How to Use an SMI
- Preparation:
- Remove the cap and check the mouthpiece for any debris.
- Prime the inhaler if it’s the first use or hasn’t been used in a while.
- Using the Inhaler:
- Hold the inhaler upright.
- Breathe out fully.
- Place the mouthpiece in your mouth and seal your lips around it.
- Press the dose-release button while inhaling slowly and deeply through your mouth.
- Holding Your Breath:
- Remove the inhaler and hold your breath for about 10 seconds.
- Breathe out slowly.
- Cleaning:
- Clean the mouthpiece with a damp cloth regularly.
How to Use a Nebulizer
Nebulizers
Nebulizers convert liquid medication into a mist that can be inhaled through a mouthpiece or mask, making them ideal for individuals who have difficulty using MDIs or DPIs.
How to Use a Nebulizer
- Preparation:
- Assemble the nebulizer according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Add the prescribed medication to the medication cup.
- Attach the mouthpiece or mask.
- Using the Nebulizer:
- Sit upright in a comfortable position.
- Place the mouthpiece in your mouth or the mask over your nose and mouth.
- Turn on the machine to start the mist.
- Breathe in slowly and deeply until all the medication is used (usually takes 10-15 minutes).
- Cleaning:
- Disassemble and clean the nebulizer components after each use to prevent infection and ensure proper functioning.
Tips for Effective Inhaler Use
- Follow Your Doctor’s Instructions:
- Always use the inhaler as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
- Do not adjust your dosage without consulting your doctor.
- Practice Good Inhaler Technique:
- Proper technique ensures maximum medication delivery to your lungs.
- Ask your healthcare provider to demonstrate and watch you use the inhaler to correct any mistakes.
- Regular Cleaning:
- Keep your inhaler clean to prevent medication buildup and ensure effective delivery.
- Use a Spacer with MDIs:
- A spacer can help improve medication delivery by holding the aerosol cloud, giving you more time to inhale the medication deeply.
- Monitor Your Medication:
- Keep track of your medication usage and order refills before you run out.
- Check the Expiration Date:
- Make sure your inhaler is not expired. An expired inhaler may not deliver the correct dosage.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Not Shaking the Inhaler (for MDIs):
- Always shake your MDI to mix the medication properly.
- Incorrect Inhalation Technique:
- Inhaling too quickly or not deeply enough can reduce the effectiveness of the medication.
- Not Holding Your Breath:
- Holding your breath after inhalation allows the medication to settle in your lungs.
- Using a Dry Powder Inhaler Incorrectly:
- DPIs require a forceful and deep inhalation, unlike the slow and steady breath needed for MDIs.
- Skipping Doses:
- Consistency is key in managing respiratory conditions. Missing doses can lead to poor symptom control.
Troubleshooting Inhaler Problems
- Clogged Inhaler:
- If your inhaler is clogged, clean the mouthpiece thoroughly with warm water. Avoid soaking the inhaler mechanism.
- Low Medication:
- If you feel your inhaler is not delivering enough medication, check the counter (if available) or consult your pharmacist.
- Difficulty Using the Inhaler:
- If you find it challenging to use your inhaler, talk to your healthcare provider about alternative options like a nebulizer or an inhaler with a spacer.
Conclusion
Using an inhaler correctly is crucial for effective management of asthma, COPD, and other respiratory conditions. By understanding the different types of inhalers and following the proper techniques, you can ensure optimal delivery of medication to your lungs. Regular practice, cleaning, and adherence to your healthcare provider’s instructions will help you get the most benefit from your inhaler and maintain better respiratory health. If you have any concerns or difficulties, don’t hesitate to consult with your healthcare provider for further guidance and support.
You can also speak directly with a licensed pharmacist online about inhaler related questions for quick and convenient personalized answers.
Disclaimer: This website does not provide medical advice. No content on this site is intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. All content on this site is for educational and informational purposes only, does not constitute medical advice, and does not establish any kind of patient-provider or client-professional relationship by your use of this website. Although we strive to strictly provide accurate and up to date general information, content available on this site is not a substitute for professional medical advice, and you should not rely solely on the information provided here. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding medical conditions, treatments, or medications.