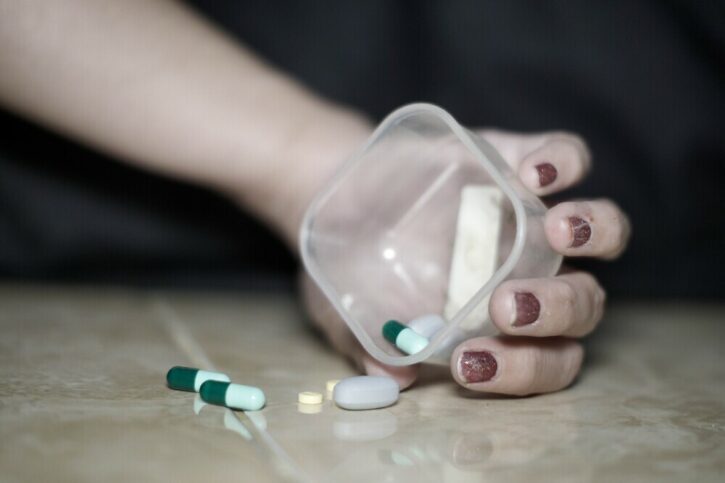
Anxiety and depression are two of the most common mental health conditions affecting millions of people worldwide. While therapy and lifestyle changes can be effective in managing these conditions, medications often play a crucial role in treatment. This comprehensive guide explores the best medications for anxiety and depression, breaking them down into different types, explaining how each works, how to use them, their costs, side effects, and what happens if you miss a dose.
After reading this guide, if you would like more information about medications used to treat anxiety and depression, you can always choose to directly talk to a pharmacist online 24/7 with Medidex Connect.
Best Medications for Anxiety and Depression by Category
There are several categories of medications used to treat anxiety and depression, including:
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
- Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)
- Benzodiazepines
- Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs)
- Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
- Atypical Antidepressants
- Beta-Blockers
- Buspirone
- Natural Supplements
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
How SSRIs Work
SSRIs increase the levels of serotonin in the brain by blocking its reabsorption (reuptake) into neurons. This helps improve mood and reduce anxiety.
Examples of SSRIs
- Fluoxetine (Prozac)
- Sertraline (Zoloft)
- Escitalopram (Lexapro)
- Paroxetine (Paxil)
- Citalopram (Celexa)
How to Use SSRIs
SSRIs are typically taken once daily, either in the morning or evening, depending on how they affect your energy levels.
Cost of SSRIs
Generic versions cost around $4 to $30 per month, while brand-name versions can be more expensive, ranging from $100 to $300 per month without insurance.
SSRI Side Effects
- Nausea
- Insomnia or drowsiness
- Dry mouth
- Increased sweating
- Sexual dysfunction
- Weight gain
Will SSRIs Stop Working if You Miss a Dose
Missing a dose of an SSRI can lead to withdrawal symptoms such as dizziness, irritability, and flu-like symptoms. If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember, unless it’s close to your next scheduled dose. Do not double up.
Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)
How SNRIs Work
SNRIs increase levels of both serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain by inhibiting their reuptake, helping to improve mood and reduce anxiety.
Examples of SNRIs
- Venlafaxine (Effexor)
- Duloxetine (Cymbalta)
- Desvenlafaxine (Pristiq)
How to Use SNRIs
SNRIs are usually taken once daily, either in the morning or evening.
Cost of SNRIs
Generic versions cost around $10 to $60 per month, while brand-name versions can range from $150 to $400 per month without insurance.
SNRI Side Effects
- Nausea
- Dry mouth
- Dizziness
- Insomnia
- Increased sweating
- Sexual dysfunction
Will SNRIs Stop Working if You Miss a Dose
Missing a dose can cause withdrawal symptoms similar to those of SSRIs. Take the missed dose as soon as you remember, unless it’s almost time for the next dose. Do not double the dose.
Benzodiazepines
How Benzodiazepines Work
Benzodiazepines enhance the effect of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the brain, producing a calming effect.
Examples of Benzodiazepines
- Alprazolam (Xanax)
- Diazepam (Valium)
- Lorazepam (Ativan)
- Clonazepam (Klonopin)
How to Use Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines are typically taken as needed for acute anxiety symptoms, but they can also be prescribed for regular use in severe cases or as a medication for insomnia to help with sleep.
Cost of Benzodiazepines
Generic versions cost around $10 to $50 per month, while brand-name versions can be significantly more expensive.
Benzodiazepines Side Effects
- Drowsiness
- Dizziness
- Confusion
- Memory impairment
- Dependence and withdrawal symptoms
Missing a Dose of Benzodiazepines
Missing a dose can lead to withdrawal symptoms, especially with long-term use. Take the missed dose as soon as you remember, unless it’s close to the next dose. Do not double up.
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs)
How Tricyclic Antidepressants Work
TCAs increase levels of norepinephrine and serotonin in the brain by blocking their reuptake, helping to improve mood and reduce anxiety.
Examples of Tricyclic Antidepressants
- Amitriptyline (Elavil)
- Nortriptyline (Pamelor)
- Imipramine (Tofranil)
How to Use TCAs
TCAs are usually taken once daily, often at bedtime due to their sedative effects.
Cost of TCAs
Generic versions cost around $10 to $50 per month.
TCA Side Effects
- Dry mouth
- Constipation
- Blurred vision
- Weight gain
- Drowsiness
- Urinary retention
Missing a Dose of TCAs
Missing a dose can lead to withdrawal symptoms and a temporary increase in anxiety and depression. Take the missed dose as soon as you remember, unless it’s close to the next dose. Do not double the dose.
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
How Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Work
MAOIs increase levels of serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine in the brain by inhibiting the enzyme monoamine oxidase, which breaks down these neurotransmitters.
Examples of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
- Phenelzine (Nardil)
- Tranylcypromine (Parnate)
- Isocarboxazid (Marplan)
How to Use Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
MAOIs are usually taken one to three times daily.
Cost of MAOIs
Generic versions cost around $20 to $100 per month.
MAOI Side Effects
- Dry mouth
- Nausea
- Insomnia
- Dizziness
- Weight gain
- Dietary restrictions to avoid hypertensive crisis
Missing a Dose of MAOI
Missing a dose can lead to withdrawal symptoms and a temporary increase in anxiety and depression. Take the missed dose as soon as you remember, unless it’s close to the next dose. Do not double the dose.
Atypical Antidepressants
How Atypical Antidepressants Work
Atypical antidepressants work through various mechanisms to affect neurotransmitters in the brain, helping to improve mood and reduce anxiety.
Examples of Atypical Antidepressants
- Bupropion (Wellbutrin)
- Mirtazapine (Remeron)
- Trazodone (Desyrel)
How to Use Atypical Antidepressants
Atypical antidepressants are usually taken once or twice daily, depending on the specific medication and dosage.
Cost of Atypical Antidepressants
Generic versions cost around $10 to $60 per month, while brand-name versions can be more expensive.
Atypical Antidepressant Side Effects
- Dry mouth
- Drowsiness
- Increased appetite and weight gain (mirtazapine)
- Insomnia (bupropion)
- Sexual dysfunction
- Dizziness
Missing a Dose of Atypical Antidepressants
Missing a dose can lead to withdrawal symptoms and a temporary increase in anxiety and depression. Take the missed dose as soon as you remember, unless it’s close to the next dose. Do not double the dose.
Beta-Blockers
How Beta-Blockers Work
Beta-blockers reduce anxiety symptoms by blocking the effects of adrenaline, slowing the heart rate, and reducing physical symptoms of anxiety.
Examples of Beta-Blockers
- Propranolol (Inderal)
- Atenolol (Tenormin)
How to Use Beta-Blockers
Beta-blockers are usually taken as needed for situational anxiety, such as performance anxiety.
Cost of Beta-Blockers
Generic versions cost around $4 to $30 per month, while brand-name versions can be more expensive.
Beta-Blocker Side Effects
- Fatigue
- Cold hands and feet
- Dizziness
- Depression
- Shortness of breath
Missing a Dose of Beta-Blockers
Missing a dose may lead to a temporary increase in anxiety symptoms. Take the missed dose as soon as you remember, unless it’s close to the next dose. Do not double the dose.
Buspirone
How Buspirone Works
Buspirone affects serotonin and dopamine receptors in the brain, which helps reduce anxiety over time.
How to Use Buspirone
Buspirone is usually taken two to three times daily, with or without food.
Cost of Buspirone
Generic buspirone costs around $10 to $40 per month.
Buspirone Side Effects
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Headache
- Nervousness
- Lightheadedness
Missing a Dose of Buspirone
Missing a dose may lead to an increase in anxiety symptoms. Take the missed dose as soon as you remember, unless it’s close to the next dose. Do not double the dose.
Natural Supplements
1. L-Theanine
How L-Theanine Works: L-Theanine is an amino acid found in tea leaves that promotes relaxation and reduces anxiety by increasing GABA, serotonin, and dopamine levels in the brain.
How to Use L-Theanine: Typically taken in doses of 200-400 mg per day.
Cost of L-Theanine: Around $10 to $30 per bottle, depending on the brand and dosage.
L-Theanine Side Effects: Generally well-tolerated with minimal side effects.
Missing a Dose of L-Theanine: Missing a dose may lead to a temporary increase in anxiety. Take the missed dose as soon as you remember, unless it’s close to the next dose.
2. Omega-3 Fatty Acids
How Omega-3 Fatty Acids Work: Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil, may help reduce anxiety and depression by decreasing inflammation and promoting healthy brain function.
How to Use Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Typically taken in doses of 1-3 grams per day.
Cost of Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Around $10 to $30 per bottle, depending on the brand and dosage.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids Side Effects: May include fishy aftertaste and gastrointestinal discomfort.
Missing a Dose of Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Missing a dose may not have immediate effects but maintaining consistent intake is recommended for long-term benefits.
3. Ashwagandha
How Ashwagandha Works: Ashwagandha is an adaptogenic herb that helps reduce stress and anxiety by modulating cortisol levels.
How to Use Ashwagandha: Typically taken in doses of 300-500 mg twice daily.
Cost of Ashwagandha: Around $15 to $40 per bottle, depending on the brand and dosage.
Ashwagandha Side Effects: Generally well-tolerated but may include gastrointestinal discomfort.
Missing a Dose of Ashwagandha: Missing a dose may lead to a temporary increase in anxiety and depression. Take the missed dose as soon as you remember, unless it’s close to the next dose.
Choosing the Right Medication for Anxiety and Depression
When selecting a medication for anxiety and depression, consider the following factors:
- Type and Severity of Symptoms: Different medications may be more effective for different types of anxiety and depression disorders.
- Side Effects: Consider potential side effects and how they may impact your daily life.
- Other Health Conditions: Some medications may interact with other conditions or medications you are taking.
- Cost: Consider the cost of medication, especially if you do not have insurance coverage.
- Personal Preference: Some people may prefer natural supplements or non-medication treatments.
Conclusion
Finding the best medication for anxiety and depression involves understanding the various options available and considering how each fits with your unique situation. Whether you opt for SSRIs, SNRIs, benzodiazepines, or natural supplements, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your needs. Regular follow-ups and adjustments may be necessary to ensure optimal results and minimize side effects. Remember, the goal is to find a treatment that helps you lead a healthier, more balanced life.
You can also always directly speak to a licensed pharmacist 24/7 with Medidex Connect to get convenient, personalized, and trustworthy answers to your medication questions such as those about the best medications for anxiety and depression as well as their side effects, interactions, and any other info you are looking for.
Disclaimer: This website does not provide medical advice. No content on this site is intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. All content on this site is for educational and informational purposes only, does not constitute medical advice, and does not establish any kind of patient-provider or client-professional relationship by your use of this website. Although we strive to strictly provide accurate and up to date general information, content available on this site is not a substitute for professional medical advice, and you should not rely solely on the information provided here. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding medical conditions, treatments, or medications.