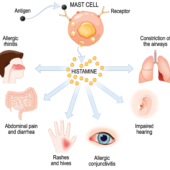
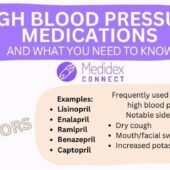
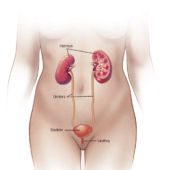
How to Manage and Treat Insomnia?
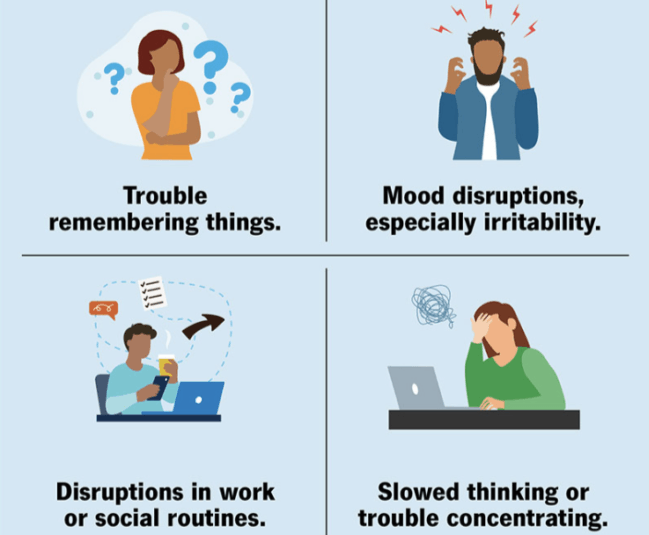
What is Insomnia? Insomnia is a common sleep disorder that can manifest as difficulty falling asleep (sleep latency), trouble staying asleep (sleep maintenance), or insufficient rest from sleep (sleep quality). Nonprescription and prescription medications are available to help manage and treat insomnia. Once you’re done reading, if you have more