What is Insomnia?
Insomnia is a common sleep disorder that can manifest as difficulty falling asleep (sleep latency), trouble staying asleep (sleep maintenance), or insufficient rest from sleep (sleep quality). Nonprescription and prescription medications are available to help manage and treat insomnia.
Once you’re done reading, if you have more questions about insomnia and how to manage insomnia symptoms, ask a pharmacist online 24/7 using Medidex Connect.
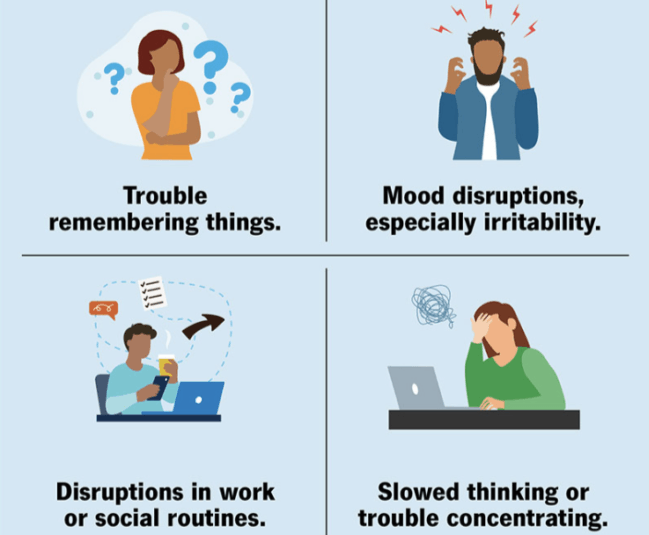
Symptoms of Sleep Insomnia?
- Remaining awake for an extended time before finally drifting off to sleep
- Getting only brief amounts of sleep
- Staying awake for a large portion of the night
- Having the sensation that you didn’t rest at all
- Rising earlier than desired
Since insomnia is often linked to other underlying health conditions, it may also help to assess whether other symptoms are present. For example, taking this schizophrenia quiz by Ubie or a bipolar disorder self-assessment can help identify patterns such as hallucinations, paranoia, extreme mood swings, or disorganized thinking, which may contribute to sleep disturbances. Similarly, conditions like generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) can lead to excessive worry and restlessness, making it difficult to fall or stay asleep. A self-assessment for anxiety can provide insight into whether persistent stress and nervousness are affecting your sleep quality. Addressing these underlying conditions can be key to improving overall well-being.
Treatments for Insomnia?
- Lifestyle modifications, such as effective sleep practices, can alleviate acute (short-term) insomnia by facilitating sleep onset and maintenance.
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), a specific form of counseling, can effectively mitigate the anxiety associated with chronic (persistent) insomnia.
- Various pharmacological treatments are available to alleviate insomnia and support the re-establishment of a regular sleep pattern.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) to Manage and Treat Insomnia
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for Insomnia is a structured program designed to help individuals overcome sleep difficulties.
- Focuses on identifying and changing thoughts and behaviors that contribute to insomnia.
- Aims to address the underlying issues causing sleep disturbances through sleep education, cognitive restructuring, and relaxation strategies.
- Individuals can improve their sleep quality and duration by promoting healthier sleep habits and reducing sleep-related anxiety.
- CBT for insomnia is often recommended as a first-line treatment due to its effectiveness and lasting results without the use of medications.
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Sleep Medications
- Side effects: daytime drowsiness, dry mouth, constipation, and urinary retention
- How does it work?
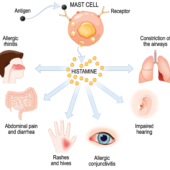
- Antihistamines block the histamine receptors in the brain, which promotes drowsiness.
- Diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
- Doxylamine (Unisom)
- Antihistamines block the histamine receptors in the brain, which promotes drowsiness.
Antidepressants to Manage and Treat Insomnia
- Side effects: dry mouth, weight gain, constipation, dizziness, blurred vision
- How does it work?
- Antidepressants are effective in promoting sleep due to their histaminergic and serotonergic properties, which facilitate sedation and enhance the overall quality of sleep.
- Mirtazapine (Remeron)
- Doxepin (Silenor)
- Trazodone (Desyrel)
- Antidepressants are effective in promoting sleep due to their histaminergic and serotonergic properties, which facilitate sedation and enhance the overall quality of sleep.
Benzodiazepines
- Side effects: Respiratory depression, drowsiness, fatigue, dizziness
- How does it work?
- Benzodiazepines are frequently utilized for short-term management of conditions that require sedation or sleep assistance due to their sedative and hypnotic effects. These medications enhance the activity of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), leading to increased sedation and muscle relaxation.
- Estazolam (ProSom)
- Flurazepam (Dalmane)
- Lorazepam (Ativan)
- Oxazepam (Serax)
- Temazepam (Restoril)
- Triazolam (Halcion)
- Benzodiazepines are frequently utilized for short-term management of conditions that require sedation or sleep assistance due to their sedative and hypnotic effects. These medications enhance the activity of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), leading to increased sedation and muscle relaxation.
Non-Benzodiazepine Sedative hypnotics (“Z” Drugs)
- Side effects: Somnolence, dizziness, ataxia (lack of coordination), parasomnias (abnormal sleep movements)
- How does it work?
- Z drugs function as agonists at the benzodiazepine-binding site of GABA receptors. This mechanism enhances their sedative effects while generally presenting fewer side effects compared to traditional benzodiazepines.
- Eszopiclone (Lunesta)
- Zaleplon (Sonata)
- Zolpidem (Ambien)
- Z drugs function as agonists at the benzodiazepine-binding site of GABA receptors. This mechanism enhances their sedative effects while generally presenting fewer side effects compared to traditional benzodiazepines.
Melatonin Receptor Agonist
- Side effects: Dizziness, nausea, vomiting, insomnia
- How does it work?
- Melatonin is a hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating the sleep-wake cycle. It is synthesized naturally by the pineal gland located in the brain.
- Ramelteon (Rozerem)
- Tasimelteon (Hetlioz)
- Melatonin is a hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating the sleep-wake cycle. It is synthesized naturally by the pineal gland located in the brain.
Orexin-Receptor Antagonist
- Side effects: Drowsiness, fatigue, headache, dizziness
- How does it work?
- Orexin, or hypocretin, is a neurotransmitter in the hypothalamus that regulates wakefulness and alertness. The body can reduce wakefulness by inhibiting orexin signals, making it easier to fall asleep and maintain sleep.
- Belsomra (Suvorexant)
- Lemborexant (Dayvigo)
- Daridorexant (Quviviq)
- Orexin, or hypocretin, is a neurotransmitter in the hypothalamus that regulates wakefulness and alertness. The body can reduce wakefulness by inhibiting orexin signals, making it easier to fall asleep and maintain sleep.

Sleep Hygiene Helps Manage and Treat Insomnia
- Establish and adhere to a consistent sleep schedule.
- Refrain from taking daytime naps, even following a night of inadequate sleep.
- Engage in relaxing activities before bedtime, such as listening to soothing music, reading, or practicing gentle stretching exercises.
- It is advisable to avoid physical exercise in the hours leading up to sleep.
- Limit the consumption of heavy meals and caffeine before bed.
Manage and Treat Insomnia – Conclusion
Sleep medications are a crucial component in the management of a variety of sleep disorders, including insomnia. While these medications can effectively improve sleep quality and duration, it is essential to carefully consider the potential risks and side effects associated with their use. A comprehensive understanding of the specific sleep disorder is vital, as each condition may respond differently to various pharmacological therapies. Additionally, individualized patient assessments are essential before initiating pharmacotherapy, considering factors such as medical history, current medications, and personal preferences. This holistic approach ensures that the benefits of sleep medication outweigh the risks, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes and improved quality of life.
If you have any additional questions about insomnia or sleep medication, connect with a licensed pharmacist on-demand with Medidex Connect.
Disclaimer: This website does not provide medical advice. No content on this site is intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. All content on this site is for educational and informational purposes only, does not constitute medical advice, and does not establish any kind of patient-provider or client-professional relationship by your use of this website. Although we strive to strictly provide accurate and up to date general information, content available on this site is not a substitute for professional medical advice, and you should not rely solely on the information provided here. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding medical conditions, treatments, or medications.